Ecology Practices

Sewage Treatment Facilities
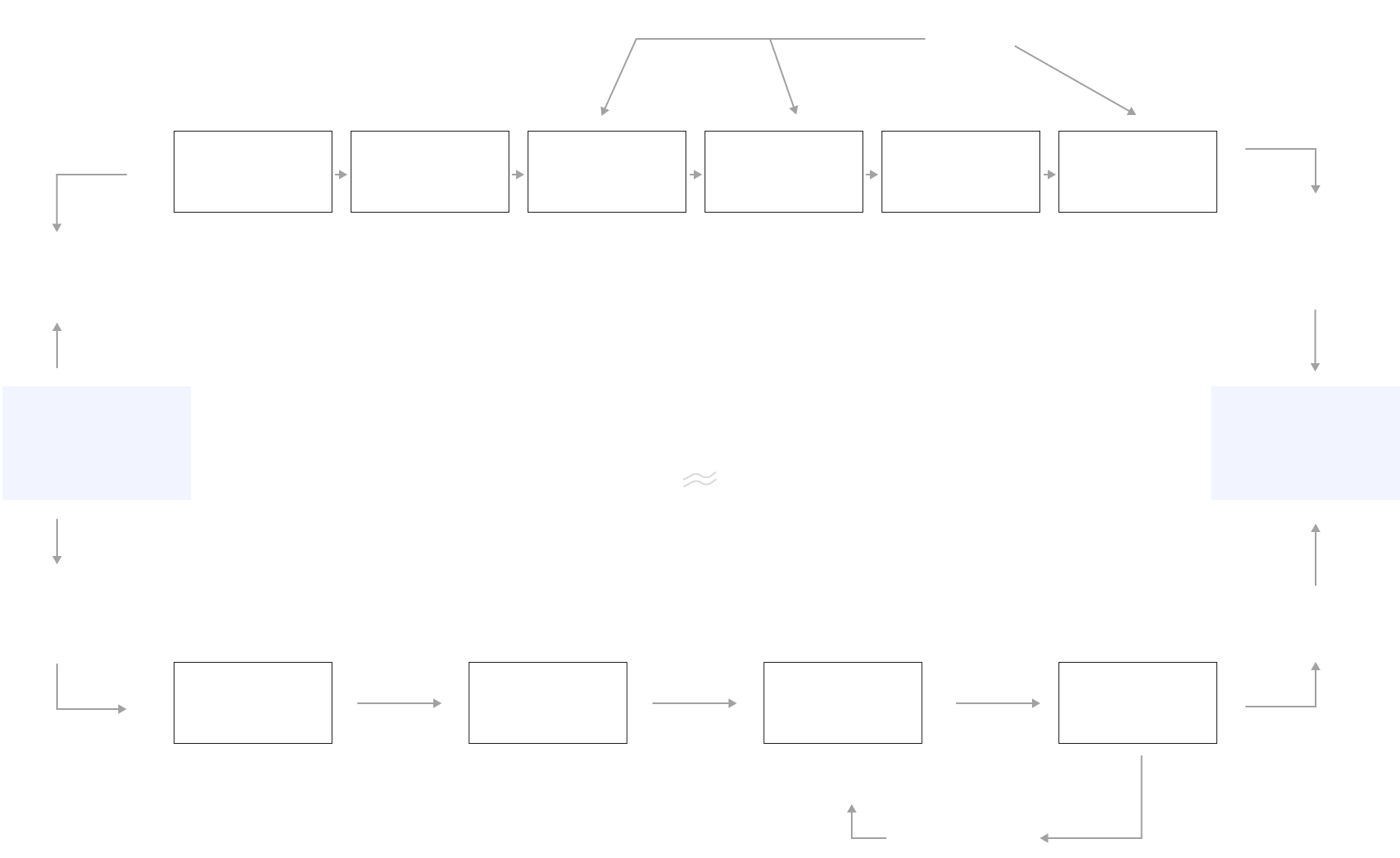
The wastewater first enters the raw water conditioning tank through mechanical grating, and then is sent to the primary sedimentation tank by lifting pump. In the primary sedimentation section by adding chemicals (coagulation / flocculation) to remove some of the organic pollutants in the wastewater, and then enter the A/O (anoxic - aerobic) biochemical system. Under the synergistic effect of aerobic bacteria, nitrifying bacteria and denitrifying bacteria, COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) is effectively degraded and biological nitrogen removal is completed. Afterwards, the wastewater enters the secondary sedimentation tank to realize mud-water separation, the reflux sludge returns to the A/O tank, and the supernatant enters the subsequent tertiary sedimentation tank. As a quality control/emergency protection unit, the tertiary sedimentation tank ensures that the effluent will continue to be discharged stably and in compliance with the standard by adding chemicals in case of system abnormality or failure.
The residual sludge produced by biochemistry and the physical sludge produced by the primary sedimentation section are dewatered by the sludge thickening tank and filter press to form sludge cake, which will be transported out for compliant disposal; the filtrate will flow back to the regulating tank for re-processing.
The wastewater first enters the raw water conditioning tank through mechanical grating, and then is sent to the primary sedimentation tank by lifting pump. In the primary sedimentation section by adding chemicals (coagulation / flocculation) to remove some of the organic pollutants in the wastewater, and then enter the A/O (anoxic - aerobic) biochemical system. Under the synergistic effect of aerobic bacteria, nitrifying bacteria and denitrifying bacteria, COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) is effectively degraded and biological nitrogen removal is completed. Afterwards, the wastewater enters the secondary sedimentation tank to realize mud-water separation, the reflux sludge returns to the A/O tank, and the supernatant enters the subsequent tertiary sedimentation tank. As a quality control/emergency protection unit, the tertiary sedimentation tank ensures that the effluent will continue to be discharged stably and in compliance with the standard by adding chemicals in case of system abnormality or failure.
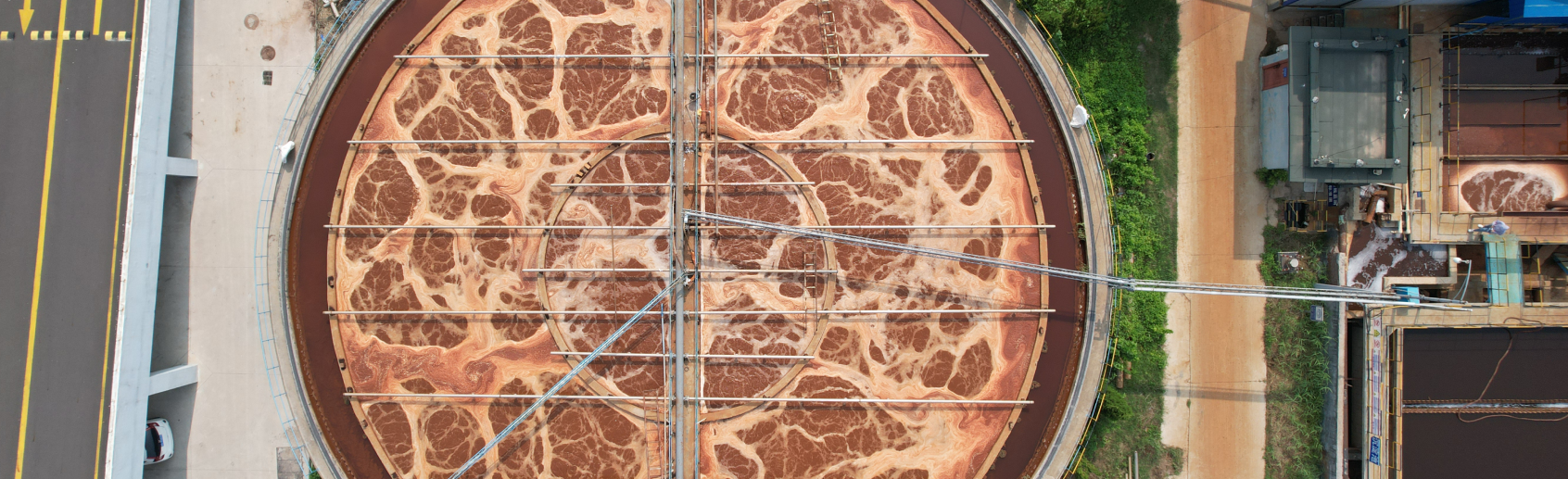

The residual sludge produced by biochemistry and the physical sludge produced by the primary sedimentation section are dewatered by the sludge thickening tank and filter press to form sludge cake, which will be transported out for compliant disposal; the filtrate will flow back to the regulating tank for re-processing.

legacy system
add medicine to a pot
reaction cell
sedimentation tank
anaerobic digestion
Sewage treatment process
sludge
parthenium (chemistry)
aerobic
precipitates
Qingshui (place name)
Online monitoring of flow tanks
Qingshui (place name)
sedimentation tank
Integrated biochemical tank
sedimentation tank
reaction cell
add medicine to a pot
all-in-one pool
regulating pool
SBR tank
sludge

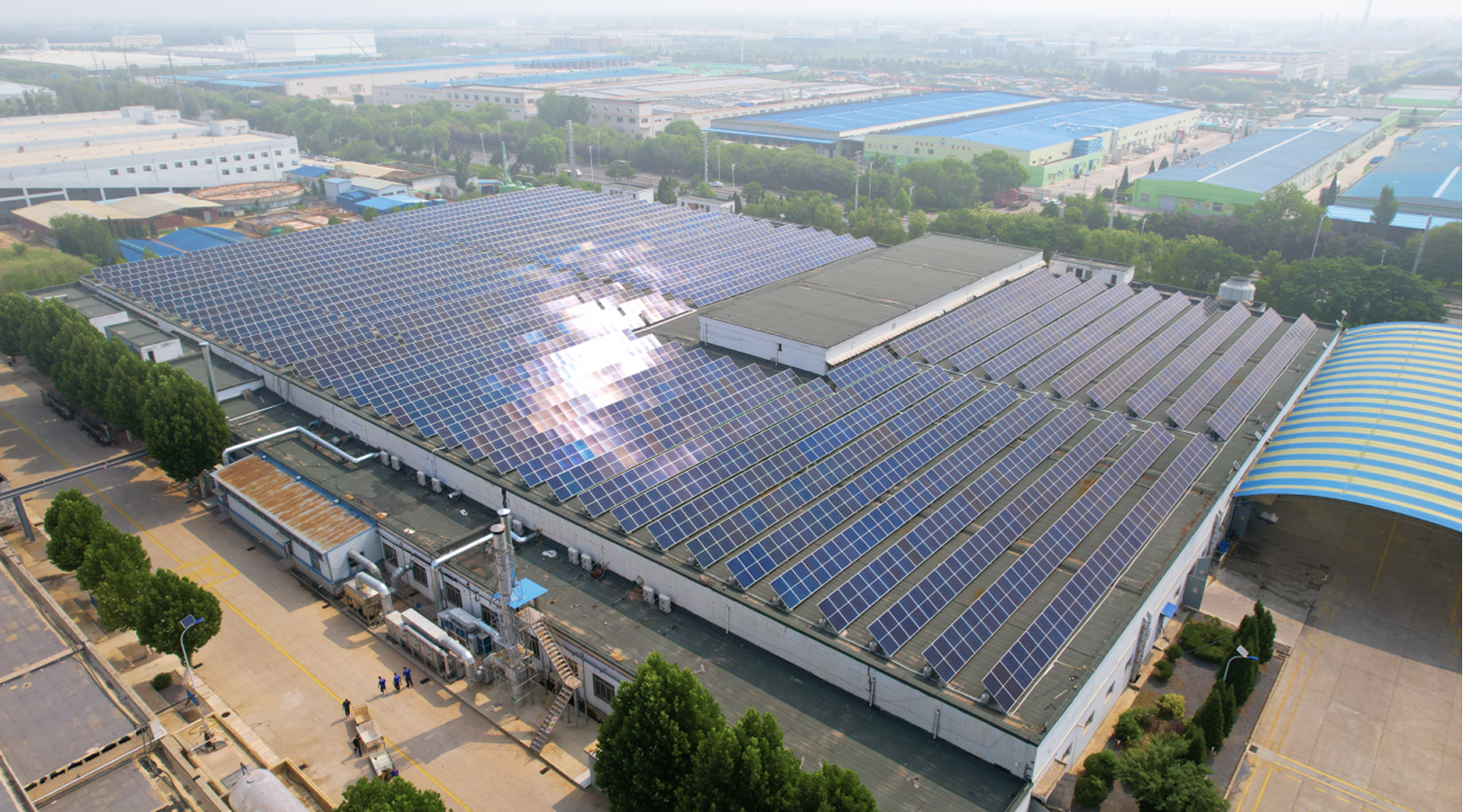
Photovoltaic (e.g. cell)
As a professional dyeing and finishing factory committed to sustainable development, we have invested in the construction of a rooftop photovoltaic power generation system, which can produce clean electricity every year, which can be directly applied to the dyeing, fixing and other high-energy-consumption production processes, realizing a reduction in the overall energy consumption of the factory by more than 25%. Through the intelligent deployment system of photovoltaic power generation and traditional energy sources, we ensure that the dyeing and finishing process is more environmentally friendly and low-carbon, and provide customers with both quality and environmentally friendly dyeing and finishing solutions.
As a professional dyeing and finishing factory committed to sustainable development, we have invested in the construction of a rooftop photovoltaic power generation system, which can produce clean electricity every year, which can be directly applied to the dyeing, fixing and other high-energy-consumption production processes, realizing a reduction in the overall energy consumption of the factory by more than 25%. Through the intelligent deployment system of photovoltaic power generation and traditional energy sources, we ensure that the dyeing and finishing process is more environmentally friendly and low-carbon, and provide customers with both quality and environmentally friendly dyeing and finishing solutions.


Sewage Discharge Information

Blue Logo + Certification
Our Mission
Bluesign helps organizations eliminate hazardous substances from their supply chains, improve their environmental and social performance, and certify products, materials, and facilities to the highest standards. Through the company's structured and data-driven approach, it supports partners in measuring, reducing and reporting on their impacts.

- Purpose
Specialized in sustainable textiles and chemicals manufacturing.
- Industry
Textile, clothing and chemical industries only.
- Focus areas
Chemical safety, resource efficiency, worker safety and environmental impacts in textile production.
- Applicability
The focus is on mills, dyers and chemical suppliers in the textile chain.
- Key criteria
Restricted Substance List (RSL) Compliance
- Water/energy efficiency
- Air/water emission control
- Occupational Health and Safety Audit Process
- End-user benefits
Audits are conducted by Bluesign-certified auditors with expertise in textiles. Ensuring safer and more sustainable textiles (low-toxicity, environmentally friendly processes)
Taroko is looking forward to
Work with you






